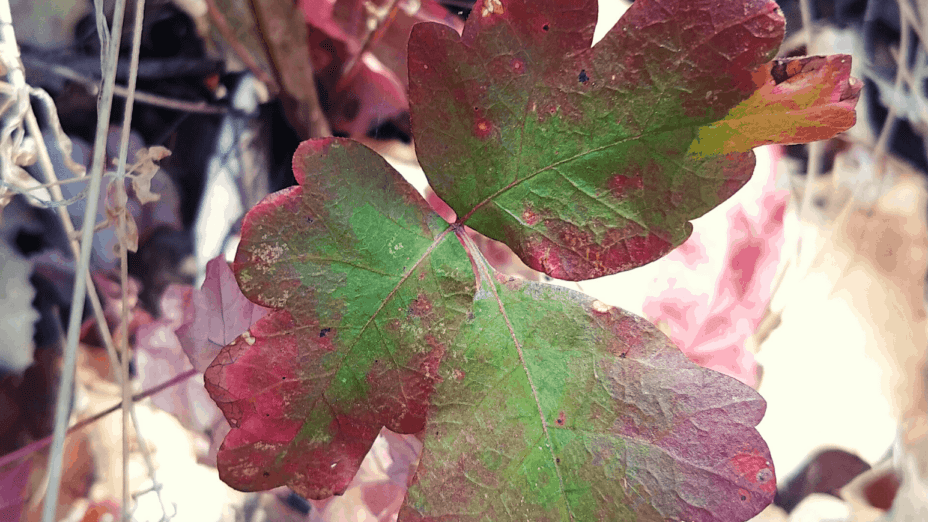
Common name: Poison oak
Scientific name: Toxicodendron diversilobum
Plant family: Anacardiaceae
Origin: California native
Duration: Perennial
Flower color: White
Plant type: Vine/shrub
Habitat: Grows in a wide range of habitats, including open woodland, grassy hillsides, dense forests
Flower attributes: Small and yellow-green. Both flowers and seeds hang in clusters
Leaf attributes: Alternate, usually appear in leaflets of three. Leaflets are reddish-green in early spring but turn green in the summer. In the autumn, leaves turn brilliant red or yellow and fall off in the winter.
Poison oak has two distinct forms: an erect shrub, three to 10 feet tall, and a climbing vine.
All parts of the plant are toxic to humans, causing dermatitis. If you get exposed, wash your skin with soap and water right away to get the plant’s oils off your skin. Some experts say that washing within the first hour may help limit the rash. The rash often shows up in lines or streaks along with blisters or large raised areas. In some people, it causes serious symptoms such as swelling and widespread, large, oozing blisters. Home treatment will often relieve mild symptoms. Prescription medicine may be needed for severe reactions.
Resources:

